Horses have captivated human imagination for millennia, symbolizing freedom, power, and grace. Understanding their behavior is crucial for anyone who works with or appreciates these magnificent animals. Equine behavior is a complex interplay of instinct, learning, and environmental influences. By delving into their social structures, communication methods, and natural instincts, we can foster better relationships and improve their well-being. Explore a wide range of courses on casa design, architecture, and construction at our website. Enroll today to enhance your skills and knowledge.
Social Structures and Hierarchies
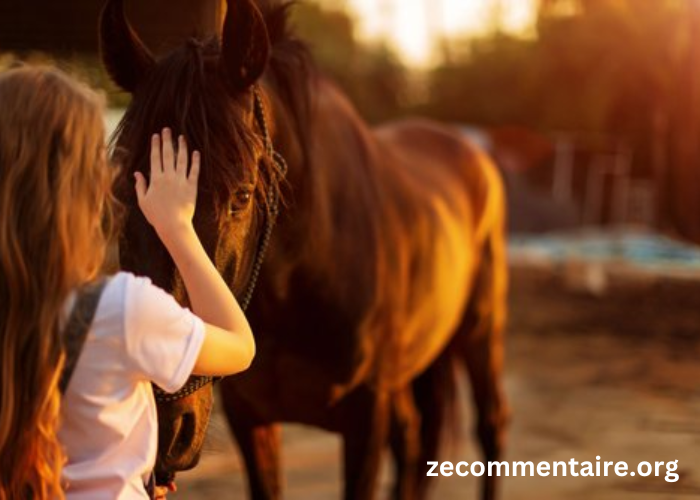
Horses are highly social animals, thriving in herds with well-defined social structures. In the wild, these herds are typically led by a dominant mare, who guides the group and makes crucial decisions. The stallion, often seen as the protector, defends the herd from threats. Understanding this hierarchy is essential for managing domestic horses. They naturally seek a leader, and in the absence of a clear human leader, they might become anxious or unruly.
In domestic settings, horses often form bonds with other horses and even humans. These bonds are critical for their mental health. Isolation can lead to stress and behavioral issues. Providing opportunities for social interaction, whether with other horses or through consistent human companionship, helps maintain their psychological well-being.
Communication: The Silent Language
Horses communicate primarily through body language. Ears, eyes, and tails are the main indicators of their mood and intentions. For instance, pinned ears can signify aggression or discomfort, while forward ears indicate curiosity or attentiveness. Understanding these cues can prevent misunderstandings and ensure safer interactions.
Vocalizations also play a role, though less prominent than body language. Whinnies, nickers, and snorts each have distinct meanings. A nicker, often a low-pitched sound, is generally a sign of affection or greeting. Recognizing these sounds and their contexts helps in building a deeper connection with the horse.
Instincts and Natural Behaviors
Horses are prey animals, and their behavior is deeply rooted in survival instincts. Flight is their primary response to perceived threats. This instinct explains why horses can sometimes seem skittish or easily spooked. Creating a calm and predictable environment can help mitigate these reactions. Gradual exposure to new stimuli, known as desensitization, is an effective method to help horses overcome fear.
Grazing is another natural behavior. In the wild, horses spend a significant portion of their day grazing, which is crucial for their digestive health. Domesticated horses benefit from a diet and routine that mimic this natural grazing pattern. Providing ample forage and allowing for regular, small meals can prevent issues like colic and ulcers.
Training and Learning
Training a horse requires patience, consistency, and an understanding of their learning processes. Horses learn through reinforcement, where behaviors are shaped by rewards and consequences. Positive reinforcement, such as treats or praise, encourages desired behaviors. Conversely, negative reinforcement involves the removal of an unpleasant stimulus when the desired behavior is performed.
It’s important to note that horses do not respond well to harsh punishment. Such methods can lead to fear and aggression, undermining trust and cooperation. Gentle, clear communication and consistent boundaries are key to effective training.
The Human-Equine Bond
The relationship between humans and horses is a testament to the deep bond that can form between species. This connection goes beyond mere utility; it encompasses companionship, mutual respect, and emotional support. Horses have been used in therapeutic settings, aiding in the treatment of physical, emotional, and psychological conditions. The presence of a horse can have a calming effect, helping individuals develop confidence and emotional resilience.
Conclusion
Understanding equine behavior is not just about improving training outcomes or ensuring safety. It’s about fostering a deeper appreciation for these remarkable animals. By learning to read their cues, respecting their instincts, and providing for their social and physical needs, we can create environments where horses thrive. This understanding ultimately enriches the human-equine bond, leading to more rewarding and harmonious interactions. Whether you are a seasoned equestrian or a casual admirer, delving into the world of equine behavior offers invaluable insights into the majestic world of horses.