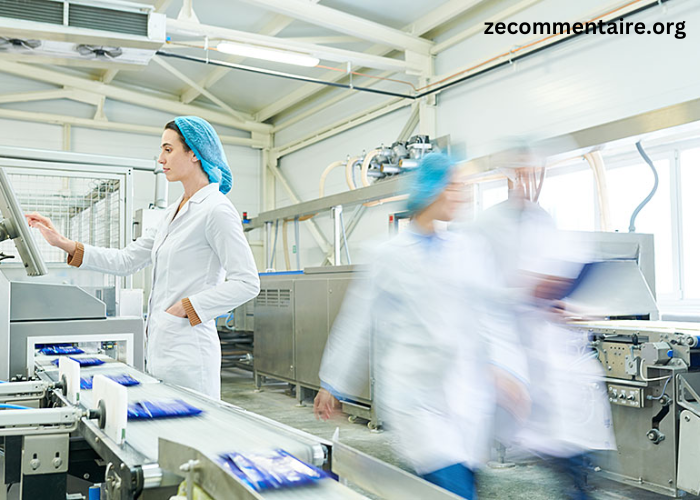
In today’s rapidly evolving food industry, maintaining a contamination-free environment is more crucial than ever. As consumer demand for high-quality, safe food products grows, food processing facilities must adopt stringent hygiene practices to prevent contamination. Contamination can have severe consequences, from causing foodborne illnesses to triggering costly recalls and damaging brand reputation. To mitigate these risks, implementing best practices for preventing contamination is essential. This article will explore the key strategies food processing facilities can use to maintain a safe and hygienic environment.
1. Implementing Robust Sanitation Protocols
A cornerstone of preventing contamination in food processing is the establishment of robust sanitation protocols. Regular cleaning and sanitization of all surfaces, equipment, and tools are vital to eliminate bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants that may be present. Facilities should develop a comprehensive sanitation schedule, ensuring all areas are regularly cleaned according to the specific needs of each processing stage.
The use of Clean-in-Place (CIP) systems is highly effective in maintaining cleanliness without the need to dismantle equipment. These systems use a combination of water, chemicals, and heat to clean the interior surfaces of pipes, vessels, and process equipment. To ensure maximum effectiveness, sanitation protocols must be documented, followed meticulously, and updated regularly to incorporate the latest hygiene standards and technologies.
2. Utilizing Sanitary Equipment and Design
The design of equipment used in food processing is another critical factor in preventing contamination. Equipment should be designed with hygiene in mind, minimizing crevices and areas where food particles can accumulate and bacteria can thrive. Sanitary valves, in particular, play a pivotal role in maintaining a contamination-free environment. These valves are designed to meet stringent sanitary standards, ensuring that no contaminants can enter the process stream.
Sanitary valves are specifically engineered to be easy to clean and maintain, reducing the risk of contamination. They are typically constructed from stainless steel, a material that resists corrosion and is easy to sterilize. By incorporating sanitary valves into processing lines, facilities can better control the flow of liquids and gases while maintaining high hygiene standards. This approach helps prevent the introduction of contaminants during critical processing stages, such as mixing, heating, or cooling.
3. Establishing Controlled Work Environments
Another essential practice for preventing contamination is maintaining controlled work environments. Food processing facilities should be designed to minimize the risk of cross-contamination by separating different processing areas. This can be achieved by establishing physical barriers, airlocks, and pressure differentials to prevent the movement of contaminants from one area to another.
Proper ventilation and air filtration systems are also crucial in maintaining a controlled environment. Airborne contaminants can easily spread in a processing facility, especially in areas where raw and finished products are handled. Installing high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and maintaining positive air pressure in critical areas can help prevent the introduction of airborne contaminants.
4. Implementing Strict Personal Hygiene Practices
Employee hygiene is a fundamental component of any contamination prevention strategy. Employees who work in food processing facilities should receive thorough training on personal hygiene practices, such as handwashing, the proper use of protective clothing, and how to prevent cross-contamination. Facilities should provide adequate handwashing stations equipped with antibacterial soap, sanitizers, and disposable towels.
In addition, all employees should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, hairnets, and clean uniforms, to minimize the risk of contamination. Regular monitoring and reinforcement of personal hygiene practices are essential to ensure compliance and maintain a hygienic processing environment.
5. Regular Monitoring and Testing for Contaminants
Preventing contamination in food processing facilities also requires regular monitoring and testing for potential contaminants. This includes testing raw materials, in-process products, and finished goods for microbial, chemical, and physical contaminants. Routine environmental monitoring, such as swabbing surfaces and equipment, can help identify contamination sources and ensure that sanitation practices are effective.
Facilities should establish a comprehensive testing program, selecting appropriate testing methods and frequency based on the specific risks associated with their products and processes. By identifying and addressing potential contamination issues early, facilities can prevent more significant problems down the line.
6. Implementing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs)
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) are guidelines that food processing facilities must follow to ensure that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. GMPs encompass a wide range of practices, including proper facility design, equipment maintenance, employee training, and quality control procedures. Adhering to GMPs is essential for preventing contamination and ensuring the safety and quality of food products.
Facilities should regularly audit their GMP compliance to identify areas for improvement and ensure that all employees are aware of and adhere to GMP requirements. Continuous training and education on GMPs can help reinforce the importance of hygiene and contamination prevention in food processing.
7. Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Safety
Advancements in technology have provided food processing facilities with innovative tools to enhance safety and prevent contamination. Automated systems, such as robotics and sensors, can minimize human contact with food products, reducing the risk of contamination. Real-time monitoring systems can detect potential issues before they escalate, allowing facilities to take immediate corrective action.
Moreover, implementing blockchain technology can enhance traceability and transparency throughout the supply chain, making it easier to identify the source of contamination and take corrective actions quickly. By leveraging these technologies, facilities can improve their ability to maintain a contamination-free environment.
Conclusion
Preventing contamination in food processing is a multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive approach. By implementing robust sanitation protocols, utilizing sanitary equipment, maintaining controlled environments, enforcing strict personal hygiene practices, regularly monitoring for contaminants, adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices, and leveraging technology, food processing facilities can significantly reduce the risk of contamination. As the food industry continues to evolve, adopting these best practices will be crucial in ensuring the safety, quality, and integrity of food products.
By investing in these contamination prevention strategies, food processing facilities can protect their consumers, maintain their brand reputation, and ensure compliance with food safety regulations.