When a critical machine fails in your factory, production screeches to a standstill, deadlines become mere wishful thinking, and financial losses start ticking up by the minute. At the core of many such malfunctions? The humble industrial bearing; a small but pivotal component whose failure can spell disaster for any business relying on mechanical operations.
For facility managers and maintenance professionals, the challenge isn’t just about dealing with a malfunction. It’s about preventing them before they disrupt the workflow and incur hefty costs.
This article goes into the common yet overlooked issues with industrial bearings and offers you expert tips on how to troubleshoot and prevent them. By understanding and addressing these key pain points, you can ensure that your machinery runs smoothly to keep your operations efficient and your financial losses to a minimum.
Bearing Function and Types Explained
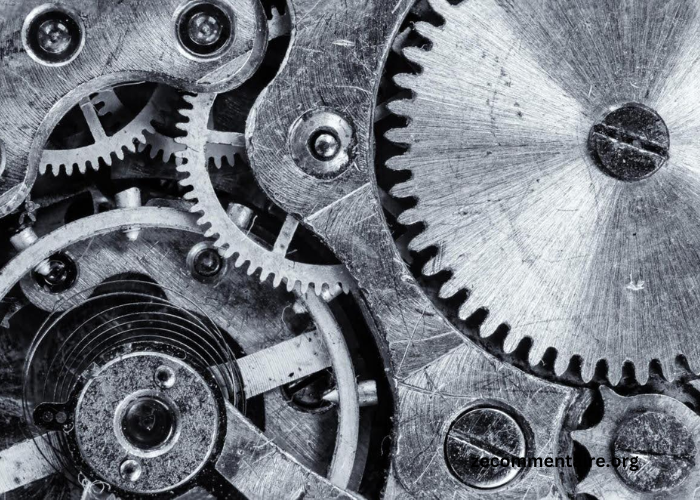
Industrial bearings are essential components that facilitate motion by reducing friction between moving parts. They support shafts that rotate within machinery to allow smooth, efficient, and reliable operation.
Without bearings, the wear and tear on equipment would be severe, leading to frequent breakdowns and costly repairs.
Bearings come in various types, each suited to specific applications. Ball bearings, one of the most common bearing types, are designed to handle both radial and axial loads. They are used in everything from electric motors to roller skates.
Roller bearings, on the other hand, are designed to carry heavy loads and are typically used in conveyor belt rollers and industrial machinery. Other types include needle bearings, which are suitable for applications with limited radial space, and thrust bearings, which are designed to handle axial loads.
Common Industrial Bearing Issues
Bearings, despite their durability, are not immune to problems. One common issue is bearing noise, often a sign of excessive vibration or misalignment.
This noise can range from a slight hum to a loud grinding sound. It can indicate that the bearing is under stress and may fail if not addressed.
Overheating is another frequent problem. Bearings can overheat due to insufficient lubrication, excessive load, or high operational speed. Overheated bearings can seize up, leading to machinery downtime and potential damage to other components.
Vibration is also a common concern. It can result from:
- Misalignment
- Imbalance
- Wear and tear on the bearing surfaces
Excessive vibration can lead to premature bearing failure and affect the overall performance of the machinery.
Wear and tear is an inevitable issue with any mechanical component. Bearings are subjected to continuous stress and load, which over time leads to surface fatigue and material degradation. This can result in pitting, spalling, or cracking of the bearing surfaces.
Misalignment is another critical issue that can significantly reduce the lifespan of bearings. When the bearing is not properly aligned with the shaft or housing, it creates uneven load distribution. This increases stress on the bearing and leads to early failure.
Troubleshooting Techniques
When facing bearing issues, a systematic approach to troubleshooting is essential. Start by listening for unusual noises, such as grinding or clicking, which can indicate a problem. Use a stethoscope or vibration analyzer to pinpoint the source of the noise.
Next, check the bearing temperature. Elevated temperatures often signal lubrication problems. Use an infrared thermometer to measure the temperature of the bearing housing. If it’s significantly higher than normal operating conditions, investigate the lubrication system for issues like inadequate grease or oil levels.
Inspect the bearing visually. Look for signs of wear, such as pitting, scoring, or discoloration. These can indicate that the bearing has been operating under excessive load or poor lubrication conditions.
Also, check for any signs of contamination, such as dirt or metal particles, which can cause premature bearing failure.
Evaluate the bearing alignment. Use a dial indicator to check the alignment of the shaft and bearing housing. Misalignment can cause uneven load distribution and lead to bearing failure. Correct any alignment issues by adjusting the positioning of the bearing or shaft.
Measure the bearing dimension. Over time, bearings can wear down and change dimension, leading to fitment issues. Use precision measuring tools to check the bearing’s dimensions against the manufacturer’s specifications.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the life of industrial bearings. One of the most effective bearing maintenance tips is to ensure proper lubrication.
Bearings require a consistent supply of lubricant to reduce friction and prevent overheating. Use the right type of lubricant specified by the manufacturer and follow a regular lubrication schedule.
Correct installation practices are equally important. During installation, make sure that the bearing is properly aligned with the shaft and housing. Use appropriate tools and techniques to avoid damaging the bearing during installation.
Regular inspections are essential to identify potential issues before they become serious problems. Conduct periodic visual inspections and use tools like vibration analyzers and infrared thermometers to monitor the condition of the bearings. Look for signs of wear, misalignment, and contamination.
Maintaining high-performance bearings also involves monitoring the operating conditions. Ensure that the machinery is not operating beyond the specified load and speed limits for the bearings. Overloading and high speeds can significantly reduce bearing life and lead to unexpected failures.
Advanced Prevention Strategies
Condition monitoring involves continuously observing the operating conditions of the bearings using sensors and diagnostic tools. This allows for the early detection of potential issues, such as temperature spikes or unusual vibrations.
Predictive maintenance technologies take condition monitoring a step further. These technologies use data analysis and machine learning to predict when a bearing might fail based on historical performance data and real-time operating conditions.
Implementing these advanced strategies requires an investment in technology and training but can significantly reduce the risk of unexpected bearing failures. It also enhances the overall reliability and efficiency of industrial equipment.
Extend the Life of Your Machinery
In this guide, we’ve walked you through the critical steps for identifying and resolving typical problems that plague industrial bearings. We’ve also shared essential preventive strategies to help you avoid these issues in the first place.
Remember, effective industrial bearing maintenance tips and regular quality checks not only prolong the life of your bearings but also enhance the overall efficiency and reliability of your industrial equipment. For more insights and advanced techniques in industrial maintenance, visit our Business section and stay ahead in maintaining your equipment at peak performance.